

Please see BNSSG HRT PRESCRIBING PATHWAY in the Formulary section for current BNSSG prescribing guidance.
Prescribing should be in line with formulary guidelines. If prescribing off-license, you should consider relevant guidelines e.g. GMC Prescribing unlicensed medicines - professional standards - GMC (gmc-uk.org)
HRT is generally contraindicated in women with current or previous oestrogen-sensitive cancers (e.g. breast, intermediate endometrial, low-grade serous ovarian) and specialist input should be sought in cases of menopausal symptoms not responding to alternative treatment options.
Please see relevant Remedy pages for further information
Other conditions will also require further considerations. Please review local and national guidance and seek Advice and Guidance or make a referral to a menopause specialist as required.
|
Estrogen Only |
Sequential |
Continuous |
Use:
|
Use:
NB: Should not be used for >5years |
Use:
|
*Please see Gynaecology conditions and HRT
Tibolone
See HRT over 60, Cardiovascular conditions and HRT
Oral HRT is first line as recommended by BMS and NICE. This is currently the first line option for those at low risk of VTE in BNSSG.
Transdermal administration of estradiol is unlikely to increase the risk of VTE or stroke above that in non-users and is associated with a lower risk compared with oral estradiol. The transdermal route should be considered the first line route of estradiol administration in women with related risk factors
Transdermal HRT is first line for women:
It should also be considered for women whose preference is transdermal HRT and those with poor symptom control with oral HRT.
Generally, the lowest estrogen dose that provides symptom relief should be used. This should be balanced by an appropriate dose of progestogen for those requiring both hormones.
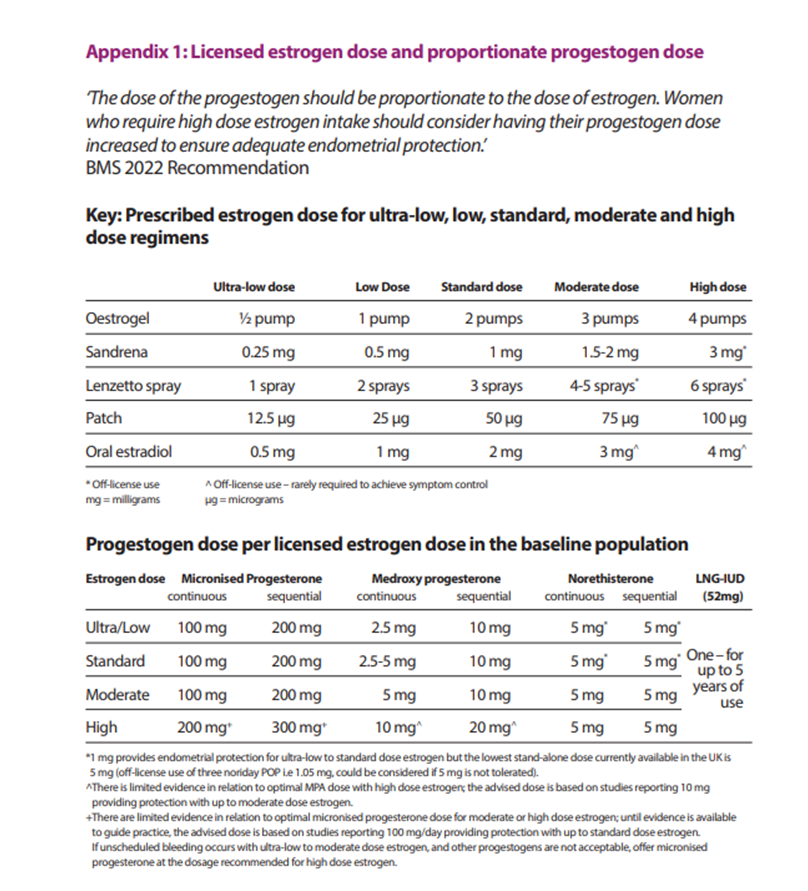
Doses should not exceed ‘high’ without specialist input. Women requiring ‘high’ dose estrogen should also have their progestogen increased. The BMS has published guidance on managing unscheduled bleeding and details appropriate doses in Appendix 1 (see below).
Management of unscheduled bleeding on hormone replacement therapy (HRT) - British Menopause Society (thebms.org.uk)
Women with POI or surgically induced menopause may require high doses.
Please also see Unscheduled Bleeding on HRT
|
Gel |
|
|
Patches |
|
|
Spray |
|
|
Micronized progesterone |
|
|
Commencing Sequential HRT |
|
Please see specific testosterone advice page
Follow up at 3 months after initiating or changing HRT:
Annual Review:
Sequential HRT should not be continued for more than 5years. You can add a diary entry to remind you to consider switching at their HRT review. GP software also has review tools you can utilise, for example Arden’s.
It is not recommended to check estradiol levels routinely. Doses should be adjusted based on symptom control.
Levels can only be interpreted for people using transdermal estradiol. If using oral estradiol, the levels cannot be interpreted and should not be taken.
If symptoms are not being controlled by an increased dose of estrogen consider:
Regulated body-identical compounds are precise duplicates of hormones. They are regulated by the MHRA. Commonly used body-identical hormones used in HRT are:
Body-identical hormones may have benefit over conventional HRT, for example improved tolerance (fewer side effects) and reduced risks (breast cancer, VTE, cardiovascular risks). However, MP use may increase the risk of breakthrough bleeding. After discussion of risks and benefits, many women choose to use body-identical preparations.
Compounded ‘bio-identical’ HRT consists of multiple hormones together (estrogens +/- progestogens +/- testosterone +/- DHEA). These are manufactured by ‘Specialist Pharmacies’ and do not follow the same regulatory pathways as conventional pharmaceutical products. Their efficacy and safety is unknown and their use is not recommended by the British Menopause Society or NICE.
Women prescribed HRT can get an HRT prescription prepayment certificate (HRT PPC). This covers all eligible HRT prescriptions for a 12month period and offers a significant discount on individual prescription costs. Most, but not all, BNSSG formulary medications are eligible. Testosterone, norethisterone/medroxyprogestrone (individually) are not eligible.
The certificate is available to buy here:
NHS Hormone Replacement Therapy Prescription Prepayment Certificate (HRT PPC) | NHSBSA
Patient Resources
Treatment for symptoms of the menopause | RCOG
Menopause and later life | RCOG
WHC factsheets and other helpful resources - Women's Health Concern (womens-health-concern.org)
NHS Hormone Replacement Therapy Prescription Prepayment Certificate (HRT PPC) | NHSBSA
BMS TV - British Menopause Society (thebms.org.uk)
https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng23/resources/menopausepdf-718895758021
https://www.womens-health-concern.org/
Find a BMS-recognised Menopause Specialist - British Menopause Society (thebms.org.uk)
Understanding Menopause for Partners - Menopause Support
References and Resources
Bioidentical HRT - British Menopause Society (thebms.org.uk)
Recommendations | Menopause: diagnosis and management | Guidance | NICE
04-BMS-TfC-HRT-Guide-NOV2022-A.pdf (thebms.org.uk)
03-BMS-TfC-HRT-Practical-Prescribing-NOV2022-A.pdf (thebms.org.uk)
Management of unscheduled bleeding on hormone replacement therapy (HRT) - British Menopause Society (thebms.org.uk)
Efforts are made to ensure the accuracy and agreement of these guidelines, including any content uploaded, referred to or linked to from the system. However, BNSSG ICB cannot guarantee this. This guidance does not override the individual responsibility of healthcare professionals to make decisions appropriate to the circumstances of the individual patient, in consultation with the patient and/or guardian or carer, in accordance with the mental capacity act, and informed by the summary of product characteristics of any drugs they are considering. Practitioners are required to perform their duties in accordance with the law and their regulators and nothing in this guidance should be interpreted in a way that would be inconsistent with compliance with those duties.
Information provided through Remedy is continually updated so please be aware any printed copies may quickly become out of date.